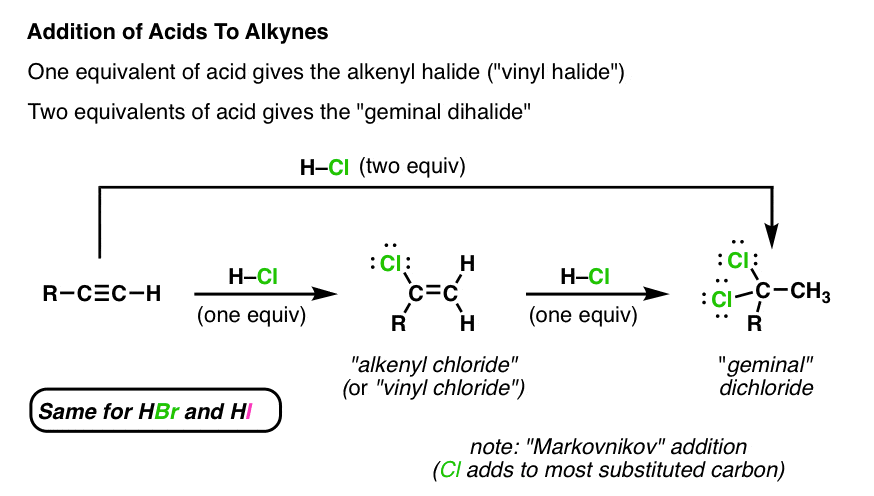Vinyl Vs Allylic Carbocation Stability
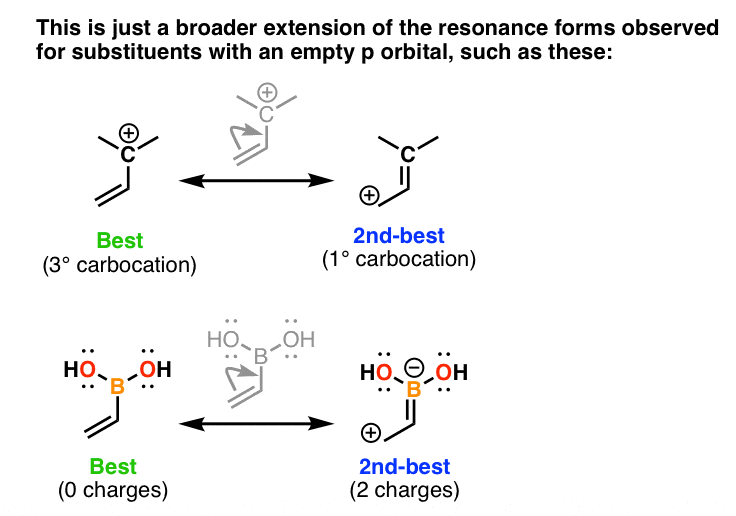
Due to the stability of the carbocation allyl compounds radially form intermediates during the reaction.
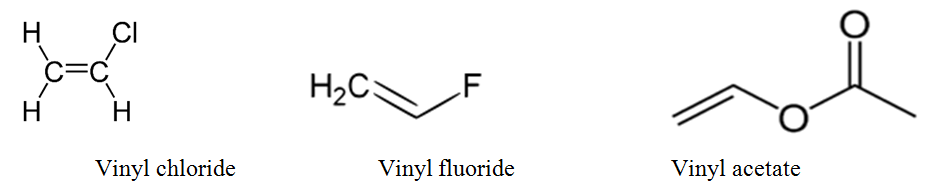
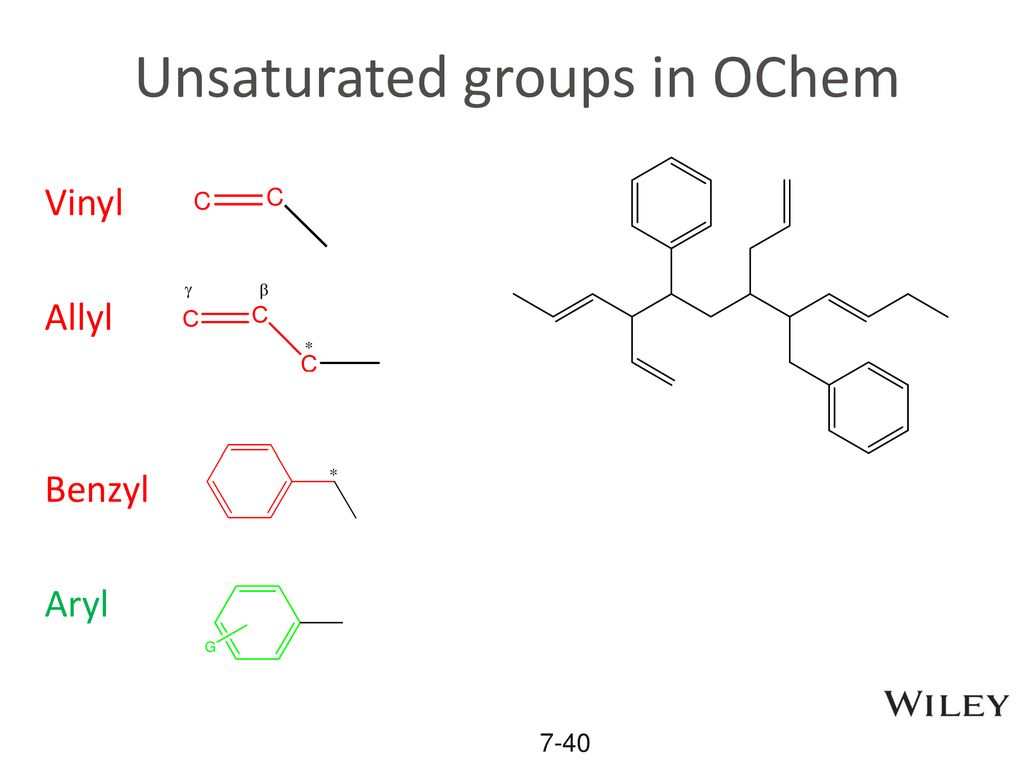
Vinyl vs allylic carbocation stability. For example s n 1 reaction. The general molecular formula is rch 2 ch ch 2. Both groups own a double bond between two carbon atoms where all the other atoms are bonded through single bonds. Its empirical formula is c 2 h 3 more generally a vinylic cation is any disubstituted trivalent carbon where the carbon bearing the positive charge is part of a double bond and is sp hybridized in the chemical literature substituted vinylic cations are often referred to as vinyl cations and understood to.
Allyl group holds three carbon atoms and five hydrogen atoms. The allyl cation is the simplest allylic carbocation. Allylic carbocations carbocation with a vinyl group as a substituent next to a double bond cc c 221 allyl carbocations are stabilized by. Allylic carbocations are able to share their burden of charge with a nearby group through resonance.
Allyl group gets attached to any other group of atoms through. Allyl groups have three carbon atoms and five hydrogen atoms. Difference between allyl and vinyl general molecular formula. Allyl form a stable carbocation because of the electron delocalization.
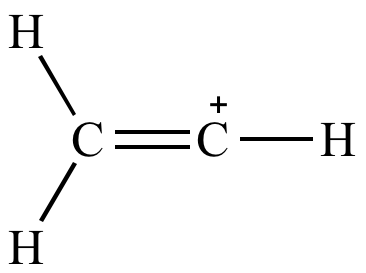
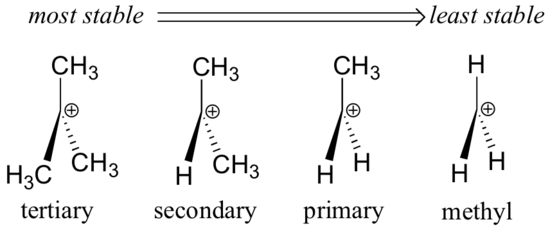
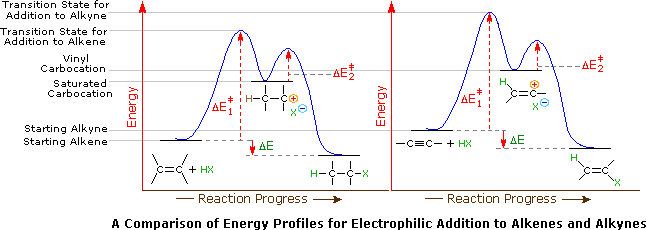
Tertiary carbocation secondary carbocation primary carbocation. In the allylic group if the allylic carbon atom carries a positive charge it forms an allylic carbocation. Vinylic carbocations are unstable as they lack p character. The rate of this step and therefore the rate of the overall substitution reaction depends on the activation energy for the process in which the bond between the carbon and the leaving group breaks and a carbocation forms.
This is very very unstable and ranks under a methyl carbocation in stability. As the allyl cation has only one substituent on the carbon bearing the positive charge it is primarily allylic carbocation. The vinyl cation is a carbocation with the positive charge on an alkene carbon. Do not confuse an allylic group with a vinyl group.
The key difference between these two structural components is the number of carbon and hydrogen atoms. Therefore the stability order of carbocation can be written as. We know that the rate limiting step of an s n 1 reaction is the first step formation of the this carbocation intermediate. Illustrates the resonance stabilization of allylic carbocation.
A vinyl carbocation has a positive charge on the same carbon as the double bond. Vinyl group has two carbon atoms and three hydrogen atoms. Stability of carbocation intermediates. Key difference allyl vs vinyl both allyl and vinyl groups have slightly similar structures with a small variation.